Kaolin is a non-metallic mineral, a type of clay and claystone dominated by kaolinite group clay minerals. Because it is white and delicate, it is also known as dolomitic clay, named after Gaoling Village in Jingdezhen, Jiangxi Province. It is pure kaolin. It is white and delicate. It is loose soil. It has good plasticity and fire resistance. It has other properties. It is mainly made of kaolinite, eclogite, mica, illite, montmorillonite, quartz, feldspar, and other minerals. Kaolin has many uses. It’s mainly used in paper, ceramics, and refractory materials. After that, it’s used in paints, rubber fillers, enamel glaze, and white cement. It’s also used in some plastics and grinding wheels. It’s in soaps, pesticides, drugs, chemicals, and building materials. It’s also in national defense and other industries.

Main processing technology of kaolin
Kaolin processing has two main steps. They are mineral processing and purification. It also includes ultrafine crushing, calcination, and surface modification. Kaolin raw ore has kaolinite group minerals as the main component. It also has varying amounts of small montmorillonite, ilmenite, alumina, quartz, feldspar, mica, and iron minerals (limonite, hematite, rhodochrosite, pyrite, etc.). It also has titanium oxides (ilmenite, rutile, etc.), organic matter (plant fibers, organic peat, coal), and other impurities. As a mineral filler application must be beneficiation and purification.
The beneficiation process of kaolin depends on the type of ore. Soft kaolin and sandy kaolin are different from hard kaolin (kaolinite). They use different beneficiation and purification processes.
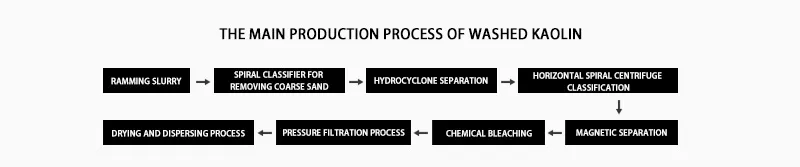
Main production process of washed kaolin
sump
Water and dispersant are added to the raw ore at a set consistency requirement, and the slurry is made in a mixer or masher. Pulping disperses kaolin and separates it from sand and plant impurities. This prepares a slurry of good consistency for the next step.
Screw Classifier to remove coarse sand
The size of quartz, feldspar, mica, and other impurities in kaolin raw ore is coarse, generally larger than 325 mesh, while kaolin is fine, mainly enriched in -2μm. Most quartz and feldspar coarse sand can be removed with a spiral classifier.
hydrocyclone sorting
The process uses hydrocyclone sorting. It removes kaolin fine sand (fine quartz, feldspar, and other impurities). It uses Ø75, Ø50, Ø25, and other different diameters of hydrocyclone for multiple sorting.
Horizontal spiral centrifuge classification
The centrifuge sorts things in a spiral. It sorts based on materials. One adjusts the process to keep the product good. They do this by changing parameters like the separation factor. At present, domestic kaolin beneficiation also has the use of hydrocyclone selection classification. Still, the flow and pressure changes make it hard to stabilize product quality at -2μm. They account for over 90% of classification efficiency. But it is not as good as horizontal spiral centrifugal classifiers.
magnetic separation
If good or high-quality kaolin is required, strong or high-gradient magnetic separation, chemical bleaching, flotation, and selective flocculation are also required in most cases. The coloring mineral impurities in kaolin, such as limonite, hematite, rhodochrosite, pyrite, anatase, rutile, etc., are weakly magnetic, so the kaolin after sand removal can be further magnetically separated by a strong magnetic separator or high gradient magnetic separator.
Because most of the iron and titanium minerals in kaolin are embedded in fine particle size, the generally strong magnetic separation often has a low removal rate, so most of the current industry uses high gradient magnetic separators for kaolin magnetic separation. In addition, better performance of the superconducting magnetic separator has also been used for kaolin magnetic separation of iron; this magnetic separator not only has magnetic field strength further improved, but you can also get a higher quality of high-quality kaolin and reduce energy consumption. If the whiteness index of kaolin after magnetic separation still cannot reach the requirement of high-quality kaolin, chemical bleaching is generally used.
The special magnetic separator for washing kaolin is a wet type strong magnetic separator with magnetic strength as high as 16000GS, which can remove the regenerated iron and improve the whiteness of kaolin during the kaolin grinding process. It can remove the regenerated iron in kaolin during the kaolin milling to improve the whiteness and other weak magnetic substances.
chemical bleaching
Bleaching chemically alters kaolin. This process is often related to the performance of kaolin and the impurities it contains. Iron minerals, titanium minerals, and organic matter are the main impurities in kaolin. They reduce its performance. People commonly use many chemical bleaching methods. These include the reduction method and the oxidation method. They also include the oxidation-reduction combined method and the acid leaching treatment method.
Filtration Process
It uses high-pressure slurry feeding. This improves productivity and keeps product moisture below 32~35%. It also saves energy and improves the work environment.
Drying and breaking process
Power drying can be used.
Currently, most of our domestic kaolin products are low-grade, and 80% can only be used in the ceramic industry. The quality and quantity of high-grade kaolin products must meet the domestic market’s requirements.
Several factors affect the whiteness of washed kaolin products. They can be analyzed from four aspects: the ore’s source, the methods used in beneficiation, the product’s granularity, and its water content.
(1) Ore source
The impurity content of washed kaolin raw ore from different origins or mining areas is different, and the corresponding whiteness will also differ. Titanium and iron compounds are the main impurities affecting the whiteness of kaolin. When the sum of the two contents exceeds 1%, its whiteness value is generally less than 85%.
Research shows that iron in kaolin exists in forms like limonite, hematite, pyrite, rhodochrosite, and ilmenite. This variety makes kaolin show different colors. These irons are in kaolin in many forms. Their combo with kaolin is also in different forms. The crystal ones are in kaolin as fine particles. The amorphous ones are on the surface of kaolin particles. They are in the form of encapsulation. The amorphous ones are the most common.
In the process, note that the same color tone ore must be processed together. The ore’s color must be strictly classified. It must be classified by the processing type. Do not mix different ore shades during processing. Only this way can ensure the ore’s purity and then improve the product’s whiteness.
(2) Beneficiation methods
First of all, the existence state of iron in kaolin must be examined correctly, so that a suitable iron removal method can be selected. There are three main categories of iron removal and whitening methods for kaolin: physical, chemical, and biological.
We usually use physical methods (re-election, flotation, magnetic separation) to enrich kaolin raw materials or remove harmful substances. First, they sort out most of the impurity minerals to purify kaolin. High gradient and superconducting magnetic separators have improved iron removal in kaolin.
But the physical method has limits. It does not work for the low content and small size of the impurity minerals. The separation effect is not clear. It also can’t separate the lattice iron. So, to get high quality, white kaolin, we can’t rely only on physical sorting.
We remove iron from minerals with chemicals. The chemicals dissolve the iron but not the other minerals. The chemical way to remove iron is very obvious. It uses the oxidation-reduction method. This method is mature and has wide use. But, it is expensive and seriously pollutes.
After comparison, it is easy to see that the chemical method has its faults. But, it is still the preferred method, in practice, because it whitens iron very well.
(3) Product granularity size
Generally, the finer the ore particle size, the higher its corresponding whiteness value. However, different uses of minerals have different particle size requirements in the actual processing. Then, further processing also increases the workload and reduces work efficiency, which could be more conducive to saving processing costs.
(4) Moisture content
Ore water content is a main factor in whiteness value. Lowering the ore’s water content can effectively improve the whiteness. So, in ore processing, we should use science and effective methods to cut the ore’s water content. This is the only way the processed ore can have higher whiteness.
Kaolin has resources for removing iron and whitening. They make it whiter and better, giving it high value. Kaolin ore types and causes vary by place. They lead to different forms of iron. To remove it, we must choose the right method for the situation. We should do many experiments to find the best way to remove the iron.

